Linked Lists
Basics
- Link
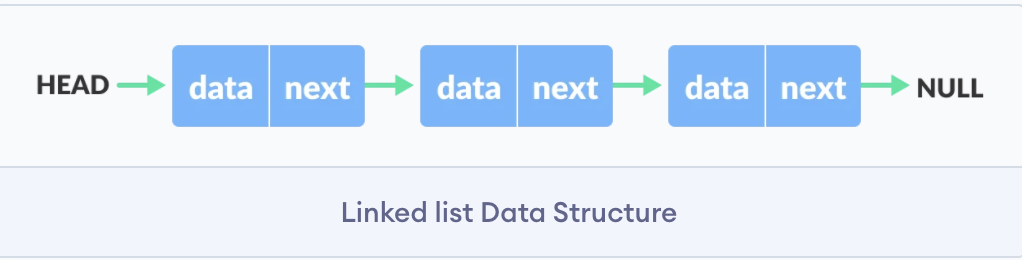
- Each link of a linked list can store a data called an element.
- Next
- Each link of a linked list contains a link to the next link called Next.
- LinkedList
- A Linked List contains the connection link to the first link called First.
Representation of Linked List:
- A data item
- An address of another node
Types of Linked List
- Simple Linked List
- Item navigation is forward only.
- Doubly Linked List
- Items can be navigated forward and backward.
- Circular Linked List
- Last item contains link of the first element as next and the first element has a link to the last element as previous.
Basic Operations
- Insertion
- Adds an element at the beginning of the list.
- Deletion
- Deletes an element at the beginning of the list.
- Display
- Displays the complete list.
- Search
- Searches an element using the given key.
- Delete
- Deletes an element using the given key.
Advantages / Disadvantages
Advantages:
- They are a dynamic in nature which allocates the memory when required.
- Insertion and deletion operations can be easily implemented.
- Stacks and queues can be easily executed.
- Linked List reduces the access time.
Disadvantages:
- The memory is wasted as pointers require extra memory for storage.
- No element can be accessed randomly; it has to access each node sequentially.
- Reverse Traversing is difficult in linked list.