Class 15 / Trees
Resources:
What is binary tree?
Binary Tree is a special datastructure used for data storage purposes. A binary tree has a special condition that each node can have a maximum of two children.
A binary tree has the benefits of both an ordered array and a linked list as search is as quick as in a sorted array and insertion or deletion operation are as fast as in linked list.
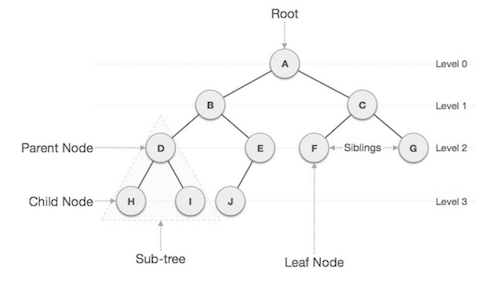
Important terms with respect to tree
- Path
- Path refers to the sequence of nodes along the edges of a tree.
- Root
- The node at the top of the tree is called root. There is only one root per tree and one path from the root node to any node.
- Parent
- Any node except the root node has one edge upward to a node called parent.
- Child
- The node below a given node connected by its edge downward is called its child node.
- Leaf
- The node which does not have any child node is called the leaf node.
- Subtree
- Subtree represents the descendants of a node.
- Visiting
- Visiting refers to checking the value of a node when control is on the node.
- Traversing
- Traversing means passing through nodes in a specific order.
- Levels
- Level of a node represents the generation of a node. If the root node is at level 0, then its next child node is at level 1, its grandchild is at level 2, and so on.
- Keys
- Key represents a value of a node based on which a search operation is to be carried out for a node.
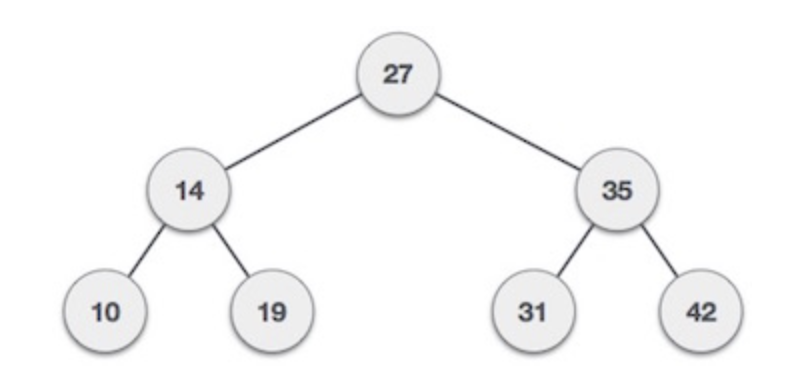
Binary Search Tree Representation
Binary Search tree exhibits a special behavior. A node’s left child must have a value less than its parent’s value and the node’s right child must have a value greater than its parent value.